In the fast-evolving landscape of technology, Cloud Computing has emerged as the linchpin for organizations seeking agility, scalability, and innovation. As Chief Information Officers (CIOs), navigating the complexities of cloud infrastructure is critical for driving digital transformation.
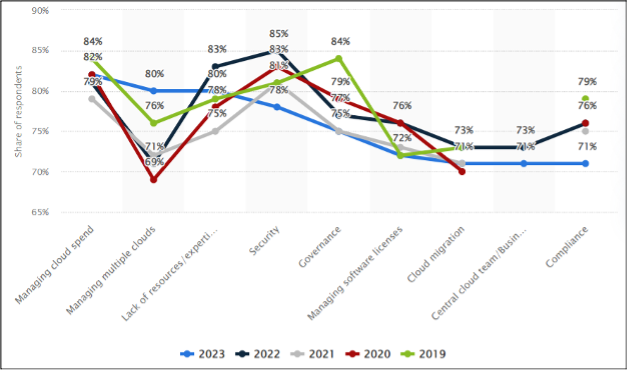
A study surveyed technical executives globally and identified the most significant challenges in cloud computing technology adoption within their organizations. Managing cloud spend emerged as the foremost challenge, with an overwhelming 82% of respondents grappling with this issue. Other challenges cited included security, governance, and a shortage of resources and expertise.
This blog delves into advanced cloud computing strategies, offering a roadmap to optimize cloud infrastructure, encompassing multi-cloud management, serverless architecture, and containerization.
Cloud Computing: Enabling Digital Transformation
Cloud computing stands as the cornerstone of digital transformation, revolutionizing the way organizations approach technology infrastructure. It serves as a catalyst for liberating enterprises from the constraints of managing physical hardware, offering a dynamic and scalable solution.
Large-scale data centers, equipped with robust processing power and expansive storage resources, empower organizations to navigate the demands of the digital era with unparalleled flexibility and efficiency. The global public cloud computing services market is not just a trend but a seismic shift in the technological landscape.
Projections indicate revenues exceeding $390 billion in 2021 and a significant surge to over $480 billion by 2022. This meteoric rise showcases the widespread acknowledgment and adoption of cloud computing as a fundamental paradigm shift.
Different Cloud Computing Models:
- Public Clouds:
- Public clouds are platforms that rent resources, including computing power and storage, to multiple clients over the internet.
- Public clouds offer unmatched scalability and digital accessibility, making them ideal for organizations with fluctuating workloads or those seeking cost-effective solutions.
- The “pay-as-you-go” model ensures efficient resource utilization.
- Private Clouds:
- Private clouds operate within the confines of an enterprise, providing dedicated resources exclusively for that organization’s use.
- Private clouds offer heightened control, security, and customization. They are particularly favored by industries with stringent compliance requirements, where data sovereignty and privacy are paramount.
- Hybrid Clouds:
- Hybrid clouds integrate components of both public and private clouds, allowing data and workloads to move seamlessly across environments.
- Hybrid cloud strategies have emerged as the preferred approach for 82% of enterprises in 2020.
- The strategic amalgamation of public and private clouds provides unparalleled flexibility.
- Organizations can leverage the scalability of the public cloud while retaining control over sensitive data and critical workloads in a private environment.
Multi-Cloud Management: Navigating Complexity for Optimal Efficiency
Adopting a multi-cloud strategy, especially for larger enterprises, necessitates adept management to maximize efficiency. While smaller companies with simpler environments find it easier to achieve high adoption rates, some enterprises with revenues exceeding $20 billion have successfully migrated 30% or more of their applications to public cloud.
Senior-management commitment and funding emerge as critical drivers of progress, as emphasized by cloud-program leaders.
Serverless Architecture: Empowering DevOps and Beyond
The Serverless Architecture market, which achieved a remarkable milestone by exceeding USD 9 billion in 2022 is a digital transformation force reshaping the technological landscape. From 2023 to 2032, this market is poised for a CAGR of over 25%.
The remarkable growth of the Serverless Architecture market is closely tied to the widespread adoption of DevOps practices. DevOps, a convergence of development and operations, has become a cornerstone for organizations aiming to enhance agility, speed, and innovation in software-based service delivery.
Within this framework, serverless computing emerges as a key enabler, streamlining processes and facilitating efficient software delivery. Contrary to its name, serverless architecture does not eliminate servers but rather redefines how infrastructure is managed.
At its core, it enables organizations to migrate computing infrastructure to the cloud, freeing them from the complexities of server management and provisioning.
Key Dimensions of Serverless Architecture:
- Efficient Resource Allocation:
- Serverless architecture optimizes resource allocation by abstracting server provisioning complexities. Resources dynamically scale based on application demands, ensuring cost-effectiveness.
- On-Demand Scalability:
- The serverless nature allows applications to scale automatically in response to varying workloads, providing organizations the flexibility to handle fluctuations in user activity seamlessly.
- Developer Focus on Coding:
- Developers in a serverless environment shift focus from infrastructure management to coding. This shift empowers developers to concentrate on creating innovative functionalities, thereby enhancing productivity.
- Cost-Efficiency with Pay-as-You-Go:
- Operating on a pay-as-you-go model, serverless computing also ensures organizations pay only for consumed computing resources, aligning with resource optimization and financial prudence.
Beyond being a technological trend, serverless architecture represents a strategic imperative in the modern technology landscape. Furthermore, it also enables CIOs to foster better talent, moving forward, and prepare their organization for new technological trends as they emerge.
Containerization: Revolutionizing Software Deployment
In 2022, a notable 16% of global survey respondents acknowledged the strategic significance of containerization in their business operations. Containerization is the process of encapsulating an application, along with its dependencies, libraries, and configuration files, within a self-contained unit known as a “container.”
This technology enables consistent and reliable execution across diverse computing environments, fostering portability, efficiency, and streamlined deployment processes. Containerization represents a fundamental shift in how software is deployed and managed.
Containers encapsulate an entire runtime environment, bundling applications along with their dependencies, libraries, and configuration files. This holistic approach to packaging makes containers an efficient form of operating system virtualization.
Key Characteristics of Containerization:
- Application Self-Sufficiency:
- Containers include applications with all necessary components, ensuring self-sufficiency and reliable execution.
- Operating System Neutrality:
- Operating independently of the host OS, containers enhance portability, flexibility, and compatibility across diverse computing environments.
- Efficient Resource Utilization:
- By sharing the host OS’s kernel, containers optimize resource usage, allowing for higher deployment density on a single host.
- Swift Deployment:
- Containers facilitate rapid deployment, streamlining development processes and accelerating the deployment pipeline.
Containers cater to a spectrum of deployment scenarios, ranging from small-scale microservices to comprehensive applications, showcasing their adaptability across various business needs. Acknowledging containerization’s strategic role reflects its crucial impact on operational efficiency and agility, while improving technological innovation.
As organizations grapple with the demands of digital transformation, containerization has emerged as a essential strategy in modern software strategies. The ability to encapsulate, deploy, and scale applications efficiently positions containerization as a cornerstone in the ever-evolving landscape of software deployment methodologies.
Conclusion: A Strategic Imperative for CIOs
As CIOs spearheading digital transformation, mastering advanced cloud computing strategies is non-negotiable. The challenges of managing cloud spend, security, and governance are formidable but surmountable with strategic foresight and robust execution. By embracing multi-cloud management, serverless architecture, and containerization, CIOs can architect resilient and scalable cloud infrastructures, driving their organizations toward unparalleled innovation and success.
In this era of technological disruption, the CIO’s handbook for Next-Gen Cloud Strategies is not just a guide; it’s a strategic imperative. The roadmap delineated herein is crafted from the experiences of navigating this terrain, ensuring that fellow CIOs can architect the future of their organizations with confidence and precision. The cloud is not just a service; it’s a strategic partner, and as CIOs, our mastery over it defines the future of our enterprises.



0 Comments